Let \(p\) be a real number such that the equation \(x^2-10 x=p\) has no real solution. of the following is true?
(A) \(0<p<25\)
(B) \(p = 25\)
(C) \(p>25\)
(D) \(p<-25\)
(E) \(-25<p<0\)
Which of the following is the largest?
(A) \(\tan 50^{\circ}+\sin 50^{\circ}\)
(B) \(\tan 50^{\circ}+\cos 50^{\circ}\)
(C) \(\sin 50^{\circ}+\cos 50^{\circ}\)
(D) \(\tan 50^{\circ}+\sin ^2 50^{\circ}\)
(E) \(\sin ^2 50^{\circ}+\cos ^2 50^{\circ}\)
Find the value of \(2021^{\left(\log {2021} 2020\right)\left(\log {2020} 2019\right)\left(\log _{2019} 2018\right)}\).
(A) 2018
(B) 2019
(C) 2020
(D) 2021
(E) None of the above
Suppose \(\sin \theta=\frac{n-3}{n+5}\) and \(\cos \theta=\frac{4-2 n}{n+5}\) for some integer \(n\). Find the maximum value of \(160 \tan ^2 \theta\).
(A) 80
(B) 90
(C) 100
(D) 120
(E) None of the above
Select all the inequalities which hold for all real values of (x) and (y).
(i) \(x \leq x^2+y^2\),
(ii) \(x y \leq x^2+y^2\),
(iii) \(x-y \leq x^2+y^2\),
(iv) \(y+x y \leq x^2+y^2\),
(v) \(x+y-1 \leq x^2+y^2 \).
(A) (i)
(B) (i) and (iii)
(C) (iii) and (iv)
(D) (ii)
(E) (ii) and (v)
Let \(x\) be the integer such that \(x=5 \sqrt{2+4 \log _x 5}\). Determine the value of \(x\).
If \(\cos A-\cos B=\frac{1}{2}\) and \(\sin A-\sin B=-\frac{1}{4}\), find the value of \(100 \sin (A+B)\).
Find the constant in the expansion of \(\left(\sqrt[3]{x}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\right)^6\left(\sqrt{x}+\frac{1}{x}\right)^{10}\).
A quadratic polynomial \(P(x)=a x^2+b x+c\), where \(a \neq 0\), has the following properties:
\(P(n)=\frac{1}{n^2} \text { for all } n=-1,2,3\). Determine the smallest positive value of \(k\), where \(k \neq 2,3\), such that \(P(k)=\frac{1}{k^2}\).
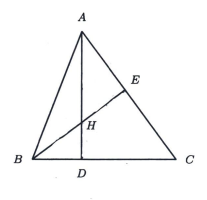
The figure below shows a triangle \(A B C\) such that \(A D\) and \(B E\) are altitudes to the sides \(B C\) and \(C A\) respectively. The lines \(A D\) and \(B E\) intersect at \(H\). Determine the area in \(\mathrm{cm}^2\) of the triangle \(A B C\) if \(A H=50 \mathrm{~cm}, D H=18 \mathrm{~cm}\) and \(B H=E H\).
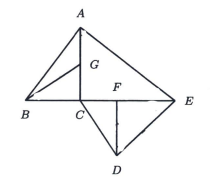
In the figure below, \(\angle G C B=\angle A C E=\angle D F E=90^{\circ}\), and \(\angle G B C=\angle E A C=\) \(\angle E D F=\theta^{\circ}\). Also, \(G B=6 \mathrm{~cm}, A E=10 \mathrm{~cm}\) and \(D E=8 \mathrm{~cm}\). Let \(\mathcal{S}\) denote the sum of the areas of the triangles \(A B C\) and \(C D E\). Find the maximum possible value of \(\mathcal{S}\) in \(\mathrm{cm}^2\) .
Find the sum of all the solutions to the equation \(\sqrt[3]{x-110}-\sqrt[3]{x-381}=1\) .
If \(f(x)=\left(2 x+4+\frac{x-2}{x+3}\right)^2\), where \(-2 \leq x \leq 2\), find the maximum value of \(f(x)\).
Given that \(D=\sqrt{\sqrt{x^2+(y-1)^2}+\sqrt{(x-1)^2+y^2}}\) for real values of (x) and (y), find the minimum value of \(D^8\).
Find the minimum value of \(\frac{8}{\sin 2 \theta}+12 \tan \theta\), where \(0<\theta<\frac{\pi}{2}\).
Determine the largest angle \(\theta\) (in degree), where \(0^{\circ} \leq \theta \leq 360^{\circ}\), such that \(\sin \left(\theta+18^{\circ}\right)+\sin \left(\theta+162^{\circ}\right)+\sin \left(\theta+234^{\circ}\right)+\sin \left(\theta+306^{\circ}\right)=1+\cos \left(\theta+60^{\circ}\right)+\cos \left(\theta+300^{\circ}\right)\).
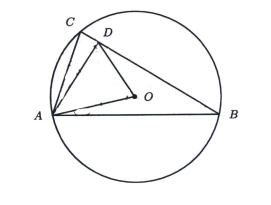
Let \(O\) be the circumcentre of the triangle \(A B C\) and that \(\angle A B C=30^{\circ}\). Let (D) be a point on the side (B C) such that the length of \(A D\) is the same as the radius of the circle. Determine the value of \(\angle A D O\) (in degree) if \(\angle O A B=10^{\circ}\).
A function \(f\) satisfies \(f(x) f(x+1)=x^2+3 x\) for all real numbers \(x\). If \(f(1)+f(2)=\frac{25}{6}) and (0<f(1)<2\), determine the value of \(11 \times f(10)\).
Find the value of
\(\frac{1}{\sin ^2 0.5^{\circ}}-\tan ^2 0.5^{\circ}+\frac{1}{\sin ^2 1.5^{\circ}}-\tan ^2 1.5^{\circ}+\frac{1}{\sin ^2 2.5^{\circ}}-\tan ^2 2.5^{\circ}+\cdots+\frac{1}{\sin ^2 179.5^{\circ}}-\tan ^2 179.5^{\circ}\) .
Let \(a_1, a_2, a_3\) be three distinct integers where \(1000>a_1>a_2>a_3>0\). Suppose there exist real numbers \(x, y, z\) such that
\(\left(a_1-a_2\right) y+\left(a_1-a_3\right) z=a_1+a_2+a_3 \)
\( \left(a_1-a_2\right) x+\left(a_2-a_3\right) z=a_1+a_2+a_3 \)
\(\left(a_1-a_3\right) x+\left(a_2-a_3\right) y=a_1+a_2+a_3\) .
Find the largest possible value of \(x+y+z\).
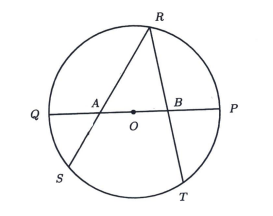
The figure below shows a circle centred at \(O\) with radius \(555 \mathrm{~cm}\). If \(O A=O B\) and \(\frac{R A}{A S}+\frac{R B}{B T}=\frac{13}{6}\), find \(O A\) (in cm).
Find the number of real solutions \(x, y\) of the system of equations
\(x^3+y^3+y^2 =0, \)
\(x^2+x^2 y+x y^2 =0\) .
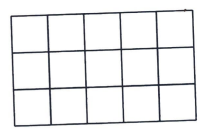
The following \(3 \times 5\) rectangle consists of \(151 \times 1\) squares. Determine the number of ways in which 9 out of the 15 squares are to be coloured in black such that every row and every column has an odd number of black squares.
Let \(n\) be a positive integer such that \(\frac{2021 n}{2021+n}\) is also a positive integer. Determine the smallest possible value of (n).
Determine the number of 5-digit numbers with the following properties:
(i) All the digits are non-zero;
(ii) The digits can be repeated;
(iii) The difference between consecutive digits is exactly 1 .