Problem 01: (Year 2023, Problem 02)
Which of the following is true?
(A) \(\sin \left(105^{\circ}\right)-\cos \left(105^{\circ}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
(B) \(\sin \left(105^{\circ}\right)-\cos \left(105^{\circ}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{2}}\)
(C) \(\sin \left(105^{\circ}\right)+\cos \left(105^{\circ}\right)=\frac{1}{2}\)
(D) \(\sin \left(105^{\circ}\right)+\cos \left(105^{\circ}\right)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
(E) None of the above.
Problem 02: (Year 2023, Problem 05)
Suppose \(\cos \left(180^{\circ}+x\right)=\frac{4}{5}\), where \(90^{\circ}<x<180^{\circ}\). Find \(\tan (2 x)\).
(A) \(\frac{24}{7}\)
(B) \(\frac{7}{24}\)
(C) \(-\frac{24}{7}\)
(D) \(-\frac{7}{24}\)
(E) \(-\frac{24}{25}\)
Problem 03: (Year 2023, Problem 13)
Let \(x\) be a real number such that
\(\frac{\sin ^4 x+\cos ^4 x}{\sin ^2 x+\cos ^4 x}=\frac{8}{11}\) .
Assuming \(\sin ^2 x>\frac{1}{2}\), find the value of \(\sqrt{28}\left(\sin ^4 x-\cos ^4 x\right)\).
Problem 04: (Year 2023, Problem 15)
Let \(C\) be a constant such that the equation \(5 \cos x+6 \sin x-C=0\) have two distint roots \(a\) and \(b\), where \(0<b<a<\pi\). Find the value of \(61 \times \sin (a+b)\).
Problem 05: (Year 2023,Problem 16)
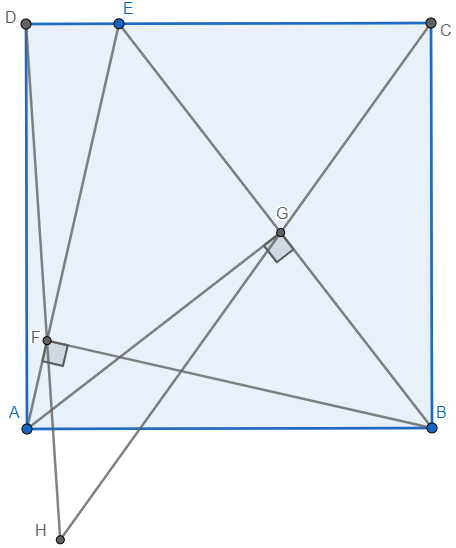
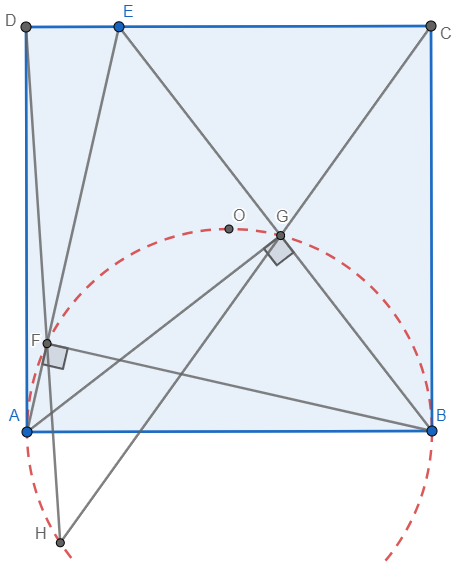
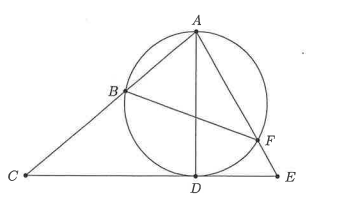
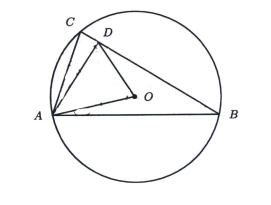
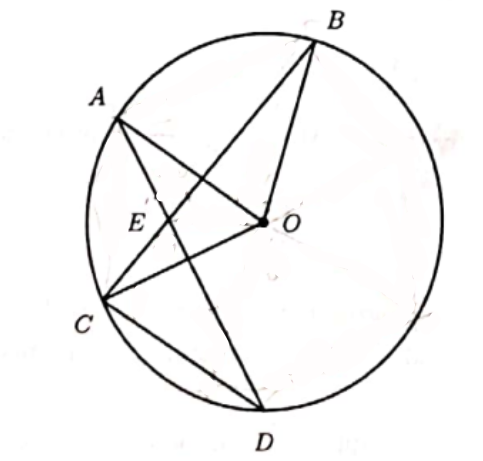
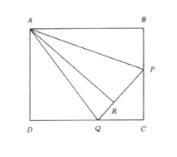
In the diagram below, \(C E\) is tangent to the circle at point \(D, A D\) is a diameter of the circle, and \(A B C, A F E\) are straight lines. It is given that \(\frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{16}{41}\) and \(\frac{A F}{A E}=\frac{49}{74}\). Let \(\tan (\angle C A E)=\frac{m}{n}\), where \(m, n\) are positive integers and \(\frac{m}{n}\) is a fraction in its lowest form. Find the sum \(m+n\).
Problem 06: (Year 2023, Problem 18)
Let \(f(x)=\cos ^2\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right)\). Find the value of
\(f \left(\frac{1}{2023}\right)+f\left(\frac{2}{2023}\right)+\cdots+f\left(\frac{2021}{2023}\right)+f\left(\frac{2022}{2023}\right)\) .
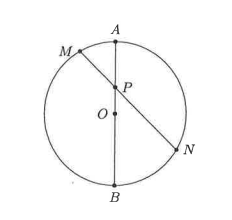
Problem 07: (Year 2023,Problem 17)
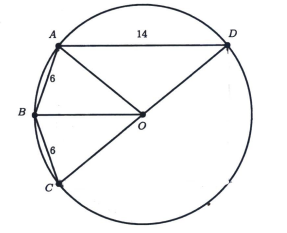
In the diagram below, \(A B\) is a diameter of the circle with centre \(O, M N\) is a chord of the circle that intersects \(A B\) at \(P, \angle B O N\) and \(\angle M O A\) are acute angles, \(\angle M P A=45^{\circ}\), \(M P=\sqrt{56}\), and \(N P=12\). Find the radius of the circle.
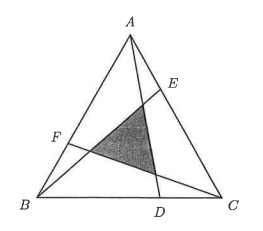
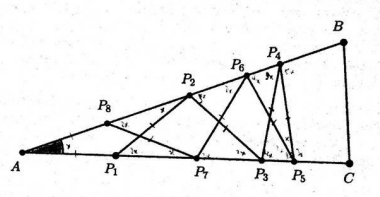
Problem 08:(Year 2023, Problem 23)
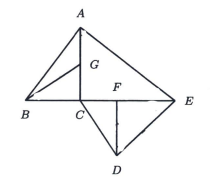
Let \(\triangle A B C\) be an equilateral triangle. \(D, E, F\) are points on the sides such that
\(B D: D C=C E: E A=A F: F B=2: 1\) .
Suppose the area of the triangle bounded by \(A D, B E\) and \(C F\) is \(2023\) . Find the area of \(\triangle A B C\).
Problem 09: (Year 2023, Problem 25)
Find the number of triangles such that all the sides are integers and the area equals the perimeter (in number).
Problem 10: (Year 2022, Problem 04)
Suppose \(y=\cos ^2 x-7 \cos x+25\), where \(x\) is any real number. Find the range of \(y\).
(A) \(17 \leq y \leq 33\)
(B) \(18 \leq y \leq 33\)
(C) \(19 \leq y \leq 33\)
(D) \(20 \leq y \leq 33\)
(E) None of the above
Problem 11: (Year 2022, Problem 05)
Suppose \(\sin \left(180^{\circ}+x\right)=-\frac{7}{9}\), where \(450^{\circ}<x<540^{\circ}\). Find \(\sin (2 x)\).
(A) \(\frac{49}{81} \sqrt{2}\)
(B) \(\frac{56}{81} \sqrt{2}\)
(C) \(-\frac{56}{81}\)
(D) \(-\frac{49}{81} \sqrt{2}\)
(E) \(-\frac{56}{81} \sqrt{2}\)
Problem 12: (Year 2022, Problem 06)
Find the value of
\(\left(\frac{\cos 10^{\circ}+\cos 50^{\circ}+\cos 70^{\circ}+\cos 110^{\circ}}{\cos 20^{\circ}}\right)^8\) .
Problem 13: (Year 2022, Problem 09)
Suppose
\(y=\frac{\tan ^2 x-\tan x+\sqrt{33}}{\tan ^2 x+\tan x+1}\),
where \(-90^{\circ}<x<90^{\circ}\). Find the maximum possible value of \(\sqrt{33}(y-5)\).
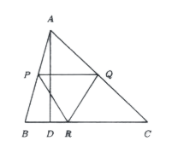
Problem 14: (Year 2022,Problem 10)
In the figure below, \(P Q R S\) is a square inscribed in a circle. Let \(W\) be a point on the arc \(P Q\) such that \(W S=\sqrt{20}\). Find \((W P+W R)^2\).
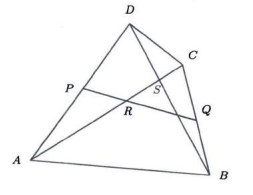
Problem 15: (Year 2022, Problem 11)
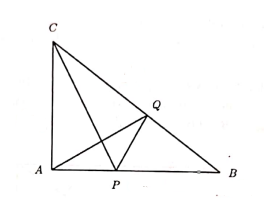
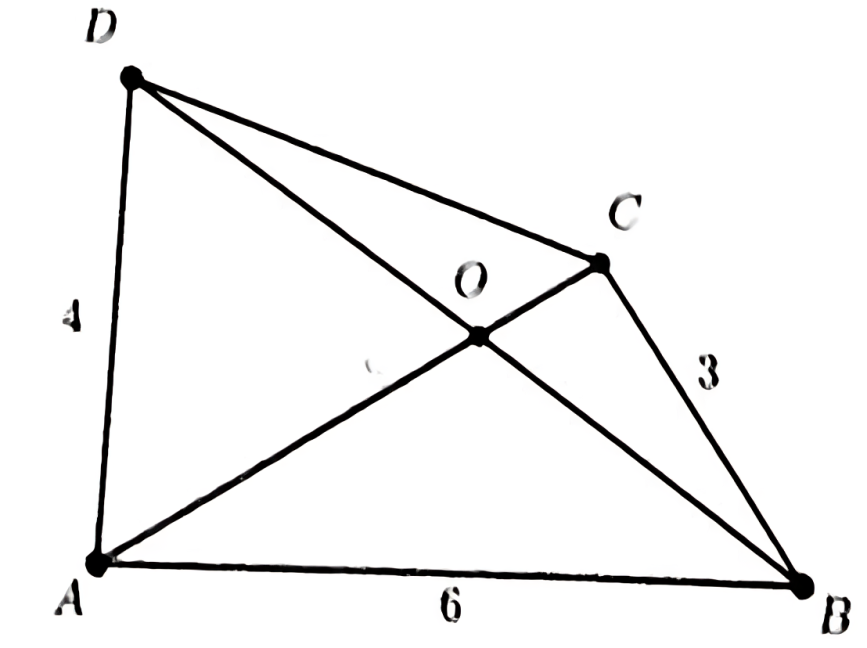
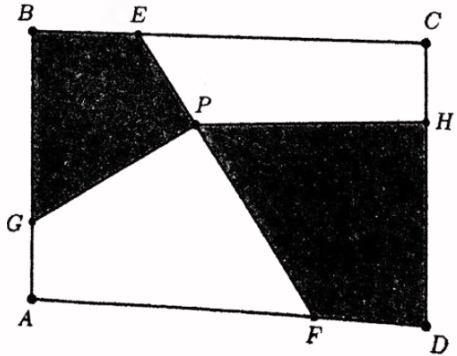
The figure below shows a quadrilateral \(A B C D\) such that \(A C=B D\) and \(P\) and \(Q\) are the midpoints of the sides \(A D\) and \(B C\) respectively. The lines \(P Q\) and \(A C\) meet at \(R\) and the lines \(B D\) and \(A C\) meet at (S). If \(\angle P R C=130^{\circ}\), find the angle \(\angle D S C\) in \({ }^{\circ})\).
Problem 16: (Year 2022, Problem 18)
Suppose
\(\cos x-\cos y =\frac{1}{2}\),
\(\sin x-\sin y =-\frac{1}{3}\)
If \(\sin (x+y)=\frac{m}{n})\), where \(\frac{m}{n}\) is expressed as a fraction in its lowest terms, find the value of \(m+n\).
Problem 17: (Year 2022, Problem 25)
Find the largest positive integer \(M\) such that \(\cos ^2 x-\sin ^2 x+\sin x=\frac{M}{888}\) has a real solution.
Problem 18: (Year 2021, Problem 02)
Which of the following is the largest?
(A) \(\tan 50^{\circ}+\sin 50^{\circ}\)
(B) \(\tan 50^{\circ}+\cos 50^{\circ}\)
(C) \(\sin 50^{\circ}+\cos 50^{\circ}\)
(D) \(\tan 50^{\circ}+\sin ^2 50^{\circ}\)
(E) \(\sin ^2 50^{\circ}+\cos ^2 50^{\circ}\)
Problem 19: (Year 2021, Problem 04)
Suppose \(\sin \theta=\frac{n-3}{n+5}\) and \(\cos \theta=\frac{4-2 n}{n+5}\) for some integer \(n\). Find the maximum value of \(160 \tan ^2 \theta\).
(A) 80
(B) 90
(C) 100
(D) 120
(E) None of the above
Problem 20: (Year 2021, Problem 07)
If \(\cos A-\cos B=\frac{1}{2}\) and \(\sin A-\sin B=-\frac{1}{4}\), find the value of \(100 \sin (A+B)\).
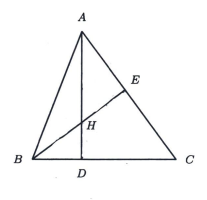
Problem 21:(Year 2021, Problem 10)
The figure below shows a triangle \(A B C\) such that \(A D\) and \(B E\) are altitudes to the sides \(B C\) and \(C A\) respectively. The lines \(A D\) and \(B E\) intersect at \(H\). Determine the area in \(\mathrm{cm}^2\) of the triangle \(A B C\) if \(A H=50 \mathrm{~cm}, D H=18 \mathrm{~cm}\) and \(B H=E H\).
Problem 22:(Year 2021, Problem 12)
In the figure below, \(\angle G C B=\angle A C E=\angle D F E=90^{\circ}\), and \(\angle G B C=\angle E A C=\) \(\angle E D F=\theta^{\circ}\). Also, \(G B=6 \mathrm{~cm}, A E=10 \mathrm{~cm}\) and \(D E=8 \mathrm{~cm}\). Let \(\mathcal{S}\) denote the sum of the areas of the triangles \(A B C\) and \(C D E\). Find the maximum possible value of \(\mathcal{S}\) in \(\mathrm{cm}^2\) .
Problem 23: (Year 2021, Problem 15)
Find the minimum value of \(\frac{8}{\sin 2 \theta}+12 \tan \theta\), where \(0<\theta<\frac{\pi}{2}\).
Problem 24: (Year 2021, Problem 16)
Determine the largest angle \(\theta\) (in degree), where \(0^{\circ} \leq \theta \leq 360^{\circ}\), such that \(\sin \left(\theta+18^{\circ}\right)+\sin \left(\theta+162^{\circ}\right)+\sin \left(\theta+234^{\circ}\right)+\sin \left(\theta+306^{\circ}\right)=1+\cos \left(\theta+60^{\circ}\right)+\cos \left(\theta+300^{\circ}\right)\).
Problem 25:(Year 2021, Problem 17)
Let \(O\) be the circumcentre of the triangle \(A B C\) and that \(\angle A B C=30^{\circ}\). Let (D) be a point on the side (B C) such that the length of \(A D\) is the same as the radius of the circle. Determine the value of \(\angle A D O\) (in degree) if \(\angle O A B=10^{\circ}\).
Problem 26: (Year 2021, Problem 19)
Find the value of
\(\frac{1}{\sin ^2 0.5^{\circ}}-\tan ^2 0.5^{\circ}+\frac{1}{\sin ^2 1.5^{\circ}}-\tan ^2 1.5^{\circ}+\frac{1}{\sin ^2 2.5^{\circ}}-\tan ^2 2.5^{\circ}+\cdots+\frac{1}{\sin ^2 179.5^{\circ}}-\tan ^2 179.5^{\circ}\) .
Problem 27:(Year 2021, Problem 21)
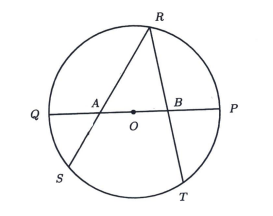
The figure below shows a circle centred at \(O\) with radius \(555 \mathrm{~cm}\). If \(O A=O B\) and \(\frac{R A}{A S}+\frac{R B}{B T}=\frac{13}{6}\), find \(O A\) (in cm).
Problem 28:(Year 2020, Problem 7)
Parallelogram \(A B C D\) has sides \(A B=39 \mathrm{~cm}\) and \(B C=25 \mathrm{~cm}\). Find the length of diagonal \(A C\) in \(\mathrm{cm}\) if diagonal \(B D=34 \mathrm{~cm}\).
Problem 29: (Year 2020, Problem 08)
Suppose \(\sin 45^{\circ}-x\)=\(-\frac{1}{3}\), where \(45^{\circ}<x<90^{\circ}\). Find \(6 \sin x-\sqrt{2})^2\).
Problem 30: (Year 2020, Problem 09)
If \(8 \cos x-8 \sin x=3\), find the value of \(55 \tan x+\frac{55}{\tan x}\).
Problem 31: (Year 2020, Problem 11)
The figure below shows a right-angled triangle \(A B C\) such that \(\angle B A C=90^{\circ}, \angle A B C=\) \(30^{\circ}\) and \(A B=48 \mathrm{~cm}\). Let \(P\) be a point on side \(A B\) such that \(C P\) is the angle bisector of \(\angle A C B\) and \(Q\) be a point on side \(B C\) such that line \(A Q\) is perpendicular to line \(C P\). Determine the length of \(P Q\).
Problem 32:(Year 2020, Problem 12)
In the figure below, the point \(O\) is the center of the circle, \(A D\) and \(B C\) intersect at \(E\), and \(\angle A E B=70^{\circ}, \angle A O B=62^{\circ}\). Find the angle \(\angle O C D\left(\right.)\) in degree \(\left.{ }^{\circ}\right)\).
Problem 33: (Year 2020, Problem 13)
Find the value of \(\frac{4 \cos 43^{\circ}}{\sin 73^{\circ}}-\frac{12 \sin 43^{\circ}}{\sqrt{3} \sin 253^{\circ}}\).
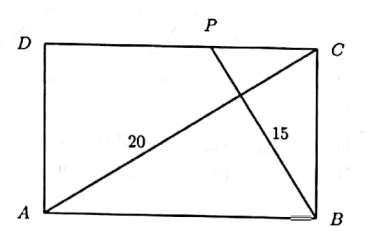
Problem 34: (Year 2020, Problem 20)
The figure below shows a rectangle (A B C D) such that the diagonal \(A C=20 \mathrm{~cm}\). Let (P) be a point on side \(C D\) such that \(B P\) is perpendicular to diagonal \(A C\). Find the area of rectangle \(A B C D\) \(in (\mathrm{cm}^2) \) if \(B P=15 \mathrm{~cm}\).
Problem 35:(Year 2020, Problem 22)
Find the number of non-congruent right-angled triangles such that the length of all their sides are integers and that the hypotenuse has a length of \(65 \mathrm{~cm}\).
Problem 36: (Year 2019, Problem 05)
Suppose that \(\sin x=\frac{12}{13}\) and \(\cos y=-\frac{4}{5}\), where \(0^{\circ} \leq x \leq 90^{\circ}\) and \(90^{\circ} \leq y \leq 180^{\circ}\). Find the value of \(\cos (x+y)\).
(A) \(-\frac{56}{65}\)
(B) \(\frac{56}{65}\)
(C) \(-\frac{16}{65}\)
(D) \(\frac{16}{65}\)
(E) None of the above
Problem 37: (Year 2019, Problem 07)
Suppose \(\tan x=5\). Find the value of \(\frac{6+\sin 2 x}{1+\cos 2 x}\).
Problem 38:(Year 2019, Problem 09 )
The coordinates of the vertices of a triangle \(\triangle A B C\) are \(A(6,0), B(0,8)\) and \(C(x, y)\) such that \(x^2-16 x+y^2-12 y+91=0\). Find the largest possible value of the area of the triangle \(\triangle A B C\).
Problem 39:(Year 2019, Problem 10)
In the figure below, \(A D\) is perpendicular to the \(B C, P Q\) is parallel to \(B C\), and the triangle \(\triangle P Q R\) is an equilateral triangle whose area in \(meter ^2\) is equal to the length of \(A D\) (in meter). Find the smallest possible value of the length of (B C).
Problem 40: (Year 2019, Problem 11)
Find the value of \(448\left(\frac{\sin 12^{\circ} \sin 39^{\circ} \sin 51^{\circ}}{\sin 24^{\circ}}\right)\).
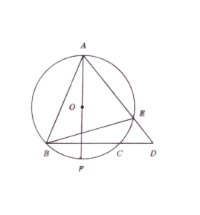
Problem 41:(Year 2019, Problem 12)
In the figure below, the chord \(A F\) passes through the origin \(O\) of the circle, and is perpendicular to the chord \(B C\). It is given that \(A B=17 \mathrm{~cm}, C D=5 \mathrm{~cm}\). Suppose \(\frac{B E}{E D}=\frac{m}{n}\), where \(m\) and \(n\) are positive integers which are relatively prime. What is the value of \(m+n\) ?
Problem 42:(Year 2019, Problem 19)
The figure below shows a rectangle \(A B C D\) with \(A B=16 \mathrm{~cm}) and (B C=15 \mathrm{~cm}\). Let \(P\) be a point on the side \(B C\) such that \(B P=7 \mathrm{~cm}\), and let \(Q\) be a point on the side \(C D\) such that \(C Q=6 \mathrm{~cm}\).
Find the length of \(A R\) \(in (\mathrm{cm})\), where \(R\) is the foot of the perpendicular from \(A\) to \(P Q\).
Problem 43:(Year 2019, Problem 21)
Consider a square \(A B C D\) on the \(x y\)-plane where the coordinates of its vertices are given by \(A(13,0), B(23,13), C(10,23)\) and \(D(0,10)\). A lattice point is a point with integer coordinates. Find the number of lattice points in the interior of the square.