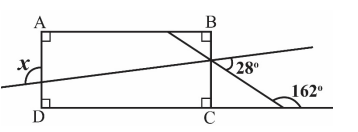
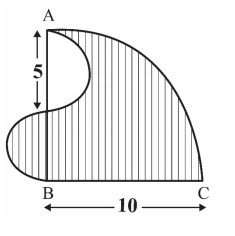
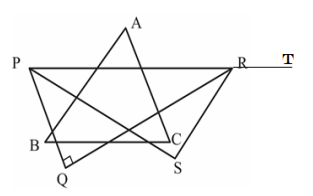
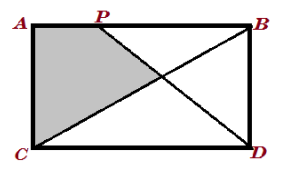
NMTC - Screening Test – Ramanujan Contest 2025
PART – A
Problem 1
If four different positive integers \(m, n, p, q\) satisfy the equation
\(7-m)(7-n)(7-p)(7-q)=4\)
then the sum \(m+n+p+q\) is equal to
A. 10
B. 24
C. 28
D. 36
Problem 2
A three member sequence \(a, b, c\) is said to be a up-down sequence if \(ac\). For example \(1,3,2\) is a up-down sequence. The sequence 1342 contains three up-down sequences: \((1,3,2),(1,4,2)\) and \((3,4,2)\). How many up-down sequences are contained in the sequence 132597684?
A. 32
B. 34
C. 36
D. 38
Problem 3
For a positive integer \(n\), let \(P(n)\) denote the product of the digits of \(n\) when \(n\) is written in base 10. For example, \(P(123)=6\) and \(P(788)=448\). If \(N\) is the smallest positive integer such that \(P(N)>1000\), and \(N\) is written as \(100 x+y\) where \(x, y\) are integers with \(0 \leq x, y<100\), then \(x+y\) equals
A. 112
B. 114
C. 116
D. 118
Problem 4
The sum of 2025 consecutive odd integers is \(2025^{2025}\). The largest of these off numbers is
A. \(2025^{2024}+2024\)
B. \(2025^{2024}-2024\)
C. \(2025^{2023}+2024\)
D. \(2025^{2023}-2024\)
Problem 5
\(A B C\) is an equilateral triangle with side length 6. \(P, Q, R\) are points on the sides \(A B, B C, C A\) respectively such that \(A P=B Q=C R=1\). The ratio of the area of the triangle \(A B C\) to the area of the triangle \(P Q R\) is
A. \(36: 25\)
B. \(12: 5\)
C. \(6: 5\)
D. \(12: 7\)
Problem 6
How many three-digit positive integers are there if the digits are the side lengths of some isosceles or equilateral triangle?
A. 45
B. 81
C. 165
D. 216
Problem 7
All the positive integers whose sum of digits is 7 are written in the increasing order. The first few are \(7,16,25,34,43, \ldots\). What is the 125 th number in this list?
A. 7000
B. 10006
C. 10024
D. 10042
Problem 8
The bisectors of the angles \(A, B, C\) of the triangle \(A B C\) meet the circum circle of the triangle again at the points \(D, E, F\) respectively. What is the value of
\(\frac{A D \cos \frac{A}{2}+B E \cos \frac{B}{2}+C F \cos \frac{C}{2}}{\sin A+\sin B+\sin C}\)
if the circum radius of \(A B C\) is 1 ?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
Problem 9
For a real number \(x\), let \(\lfloor x\rfloor\) be the greatest integer less than or equal to \(x\). For example, \([1.7]=1\) and \([\sqrt{2}]=1\). Let \(N=\left\lfloor\frac{10^{93}}{10^{31}+3}\right\rfloor\). Find the remainder when \(N\) is divided by 100.
A. 1
B. 8
C. 22
D. 31
Problem 10
A point \((x, y)\) in the plane is called a lattice point if both its coordinates \(x, y\) are integers. The number of lattice points that lie on the circle with center at \((199,0)\) and radius 199 is
A. 4
B. 8
C. 12
D. 16
Problem 11
The sum of all real numbers \(p\) such that the equation
\(5 x^3-5(p+1) x^2+(71 p-1) x-(66 p-1)=0\)
has all its three roots positive integers.
A. 70
B. 74
C. 76
D. 88
Problem 12
If \(1-x+x^2-x^3+\cdots+x^{20}\) is rewritten in the form
\(a_0+a_1(x-4)+a_2(x-4)^2+\cdots+a_{20}(x-4)^{20}\), where \(a_0, a_1, \ldots, a_{20}\)
are all real numbers, the value of \(a_0+a_1+a_2+\cdots+a_{20}\) is
A. \(\frac{5^{21}+1}{6}\)
B. \(\frac{5^{21}-1}{6}\)
C. \(\frac{5^{20}+1}{6}\)
D. \(\frac{5^{20}-1}{6}\)
Problem 13
For a positive integer \(n\), a distinct 3-partition of \(n\) is a triple \( (a, b, c) \) of positive integers such that \(a<b<c\) and \(a+b+c=n\). For example, \((1,2,4)\) is a distinct 3 -partition of 7 . The number of distinct 3-partitions of 15 is
A. 10
B. 12
C. 13
D. 15
Problem 14
If \(m\) and \(n\) are positive integers such that \(30 m n-6 m-5 n=2019\), what is the value of \(30 m n-5 m-6 n ?\)
A. 1900
B. 2020
C. 1939
D. Can not be found from the given information
Problem 15
A class of 100 students takes a six question exam. For the first question, a student receives 1 point for answering correctly, -1 point for answering incorrectly or not answering at all. For the second question, the student receives 2 points for answering correctly and -2 points for answering incorrectly or not answering at all and so on. What is the minimum number of students having the same scores?
A. 6
B. 5
C. 0
D. Can not be found from the given information
Part B
Problem 16
The value of
\(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1^2+2^2}{6}+\frac{1^2+2^2+3^2}{12}+\frac{1^2+2^2+3^2+4^2}{20}+\cdots+\frac{1^2+2^2+\cdots+60^2}{3660}\)
is ________ .
Problem 17
The largest prime divisor of \(3^{21}+1\) is _________
Problem 18
A circular garden divided into 10 equal sectors needs to be planted with flower plants that yield flowers of 3 different colors, in such a way that no two adjacent sectors will have flowers of the same color. The number of ways in which this can be done is _________
Problem 19
We call an integer special if it is positive and we do not need to use the digit 0 to write it down in base 10. For example, 2126 is special whereas 2025 is not. The first 10 special numbers are \(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11\). The 2025th special number is _________ .
Problem 20
Let \(a, b, c\) be non zero real numbers such that \(a+b+c=0\) and \(a^3+b^3+c^3=a^5+b^5+c^5\). The value of \(\frac{5}{a^2+b^2+c^2}\) is _________ .
Problem 21
The equation \(x^3-\frac{1}{x}=4\) has two real roots \(\alpha, \beta\). The value of \((\alpha+\beta)^2\) is _________
Problem 22
If \(x, y, z\) are positive integers satisfying the system of equations
\(\begin{aligned} x y+y z+z x & =2024 \ x y z+x+y+z & =2025\end{aligned}\)
find \(\max (x, y, z)\) . ________
Problem 23
If \(p, q, r\) are primes such that \(p q+q r+r p=p q r-2025\), find \(p+q+r .\). __________
Problem 24
A cyclic quadrilateral has side lengths \(3,5,5,8\) in this order. If \(R\) is its circumradius, find \(3 R^2\). __________
Problem 25
Consider the sequence of numbers \(24,2534,253534,25353534, \ldots\). Let \(N\) be the first number in the sequence that is divisible by 99 . Find the number of digits in the base 10 representation of \(N\). _____________
Problem 26
An isosceles triangle has integer sides and has perimeter 16. Find the largest possible area of the triangle. ____________
Problem 27
Suppose that \(a, b, c\) are positive real numbers such that \(a^2+b^2=c^2\) and \(a b=c\). Find the value of
\(\frac{(a+b+c)(a-b+c)(a+b-c)(a-b-c)}{c^2}\) ______________
Problem 28
In a right angled triangle with integer sides, the radius of the inscribed circle is 12. Compute the largest possible length of the hypotenuse. _______________
Problem 29
Points \(C\) and \(D\) lie on opposite sides of the line \(A B\). Let \(M\) and \(N\) be the centroids of the triangles \(A B C\) and \(A B D\) respectively. If \(A B=25, B C=24, A C=7, A D=20\) and \(B D=15\), find \(M N\). __________
Problem 30
Let \(a_0=1\) and for \(n \geq 1\), define \(a_n=3 a_{n-1}+1\). Find the remainder when \(a_{11}\) is divided by 97. ___________